Feeling depressed after vision loss?
Read more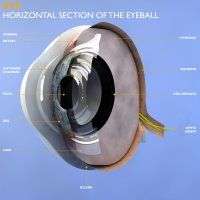
Vitreous disorders are various conditions that affect the gel-like substance (vitreous) inside the eye that helps the eye keep its round shape. Some of these conditions create only minor vision disturbances while others may be a sign of more serious eye problems. The following are some common vitreous disorders.
Vitreous Detachment
The vitreous has millions of tiny fibers running through it. These attach to the light-sensitive layer of tissue on the back of the eye, the retina.
The vitreous slowly shrinks as you grow older, which causes the fibers to tug on the surface of the retina. This does not usually cause any damage the retina because the fibers break. However, it does allow the vitreous to separate from the retina.
The main symptom of vitreous detachment is floaters in your field of vision. These appear as floating specks or “cobwebs” that dart out of the way when you try to look at them. Sometimes, you may also notice a small but sudden increase in the number of floaters accompanied by flashes of light in your side vision (i.e., peripheral vision).
Other than floaters, vitreous detachment does not usually cause any vision problems. Occasionally, though, when the fibers pull on the retina, they may create a hole in the macula or cause the retina to detach. Both of these can damage your vision and should be treated promptly.
Vitreomacular Adhesion
If the vitreous does not detach completely from the center part of the retina (macula), it can lead to a vitreomacular adhesion. (The macula is needed for sharp center vision.) If the vitreous fibers that are still attached to the macula pull hard enough, they can cause vision changes in the central vision, such as:
- Blurriness
- Decreased vision
- Vision loss in the center (in severe cases)
If you suffer from vitreomacular adhesion, your ophthalmologist may suggest waiting and monitoring the condition to determine whether symptoms get worse. If the symptoms get worse, medication or surgical intervention may become necessary to address the problem.
Uveitis
Uveitis is a type of inflammatory disease that leads to swelling and destruction of the tissues of the eye. This can affect many parts of the eye, including the vitreous, retina, optic nerve, lens and the uvea.
This condition can cause reduced vision or blindness, depending on the part of the eye that is affected. Inflammation of the vitreous, known as intermediate uveitis, has been linked to several other health conditions, such as multiple sclerosis and sarcoidosis.
What to Do If You Think You May Have a Vitreous Disorder
If you experience a sudden change in vision, including an increase in flashes of light in your side vision or in the number of floaters, have your eyes examined by your ophthalmologist right away, as this may be a sign of a serious vision problem.
If you notice gradual changes in your vision or are overdue for your routine eye exam, contact us to schedule an appointment today. Your eye health may depend on it.
-
Vision Loss and Mental Health
Category: Newsletters
-
Treatment Options for Presbyopia
Category: Newsletters
Over 40 and finding it hard to see close-up? One of these presbyopia treatment options could improve your vision.
Read more -
Summertime Allergies and Your Eyes
Category: Newsletters
-
Signs You May Have Macular Degeneration
Category: Newsletters
-
Glaucoma and You: The Importance of Eye Exams
Category: Newsletters
-
Important Healthy Eye Habits for Kids
Category: Newsletters
-
Healthy Vision Month
Category: Newsletters
-
Presbyopia eye drops
Category: Newsletters
Would you like to stop squinting when you look at close objects? A new kind of eyedrops can improve presbyopia, an age-related vision problem.
Read more -
Dry Eye
Category: Eye Symptoms
Sometimes your eyes don’t make enough tears or the tears evaporate too fast because they don’t have the right amount of compounds in them. This is called dry eye. Up to 5% of Americans complain of some form of dry eye. Individuals who wear contact lenses or have undergone LASIK or other types of
Read more -
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
Category: Common Eye Conditions, Changes in Appearance
Similar to a bruise under the skin, a subconjunctival hemorrhage happens when a small blood vessel located between the sclera (white portion of an eye) and the conjunctiva (lining on the surface of an eye) breaks and covers the sclera with blood. Unlike broken blood vessels located under the skin which
Read more -
Decorative (Plano) Contact Lenses
Category: Contact Lenses
Colored contact lenses allow you to temporarily change your eye color whether or not you need to correct impaired vision. In this way, you can create a more subtle eye appearance, wear a crazy design for special occasions, or just enjoy a new eye color. Will Colored Contacts Change the Way I See? Yes,
Read more -
Wandering Eye
Category: Pediatric Vision
A wandering eye is a type of eye condition known as strabismus or tropia, and it may be caused by damage to the retina or muscles that control the eye, stroke or brain injury, or an uncorrected refractive error like farsightedness. With a wandering eye, one eye deviates or wanders in a different direction
Read more -
Reading and Writing
Category: Pediatric Vision
For many adults, reading and writing come so naturally that they seem almost effortless. However, reading and writing are actually complicated skills that take significant effort to learn. For example, reading involves recognizing letters, associating letter combinations with their corresponding sounds,
Read more -
Dyslexia
Category: Pediatric Vision
Dyslexia When a child has difficulty reading due to problems recognizing speech sounds and learning how they connect to words and letters, the condition is known as dyslexia, a learning disorder caused by genetic traits that disturb how the brain works. It affects areas of the brain dealing with language
Read more -
Crossed Eyes
Category: Pediatric Vision
Crossed eyes, also known as strabismus, refer to a condition in which both eyes do not look at the same place at the same time. Often times they both turn in, but may also turn out. What Causes Crossed Eyes? The six muscles attached to each eye, which control how it moves, receive signals from the brain.
Read more -
Autism
Category: Pediatric Vision
Symptoms and Problems Caused By Autism Autism is a neurological disorder in which the person has difficulty processing and reacting to information received from their senses. The individual also has trouble communicating and interacting socially. Signs of autism include: Lack of shared social interaction Postponement
Read more
